
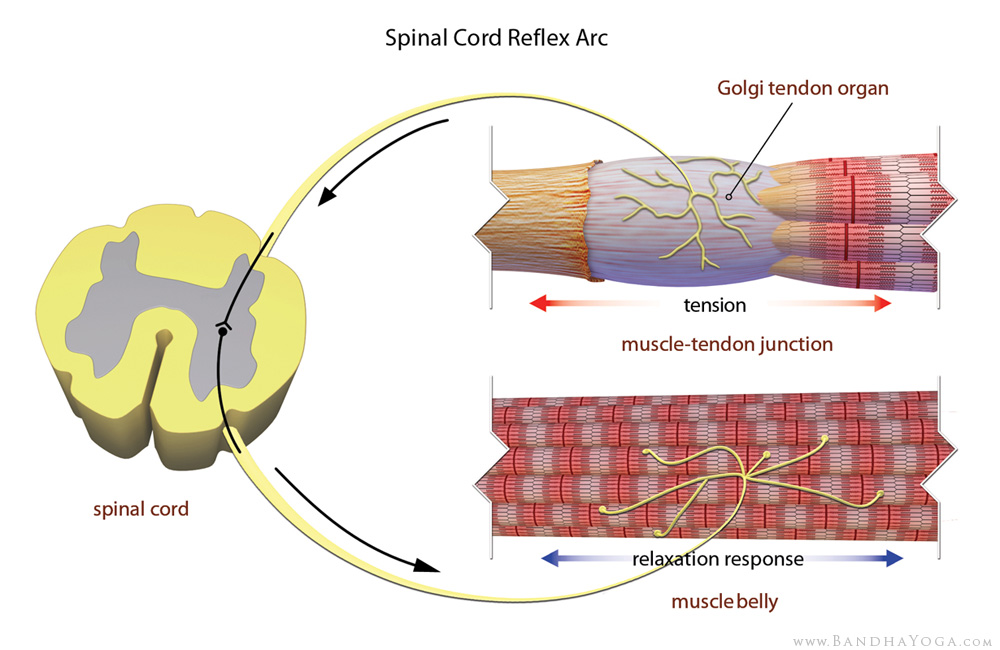
When a low-force stretch is held for more than seven seconds, the increase in muscle tension activates the GTO, which temporarily inhibits muscle spindle activity (thus reducing tension in the muscle), and allows for further stretching. Static stretching is one example of how muscle tension signals a GTO response. GTOs are sensitive to changes in tension and rate of tension and, because they are located in the musculotendinous junctions, they are responsible for sending information to the brain as soon as they sense an overload. This works in concert with the muscle spindles that monitor muscle length.
If there is too much muscle tension the golgi tendon organ will inhibit the muscle from creating any force (via a reflex arc), thus protecting the you from injuring itself. When people lift weights, the golgi tendon organ is the sense organ that tells how much tension the muscle is exerting. The myotatic reflex is caused by a stretching in the muscle spindle. This reflex, which connects high force in the Golgi tendon organs with relaxation, is the opposite of the myotatic reflex (or stretch reflex), in which stretch elicits a reflex contraction.
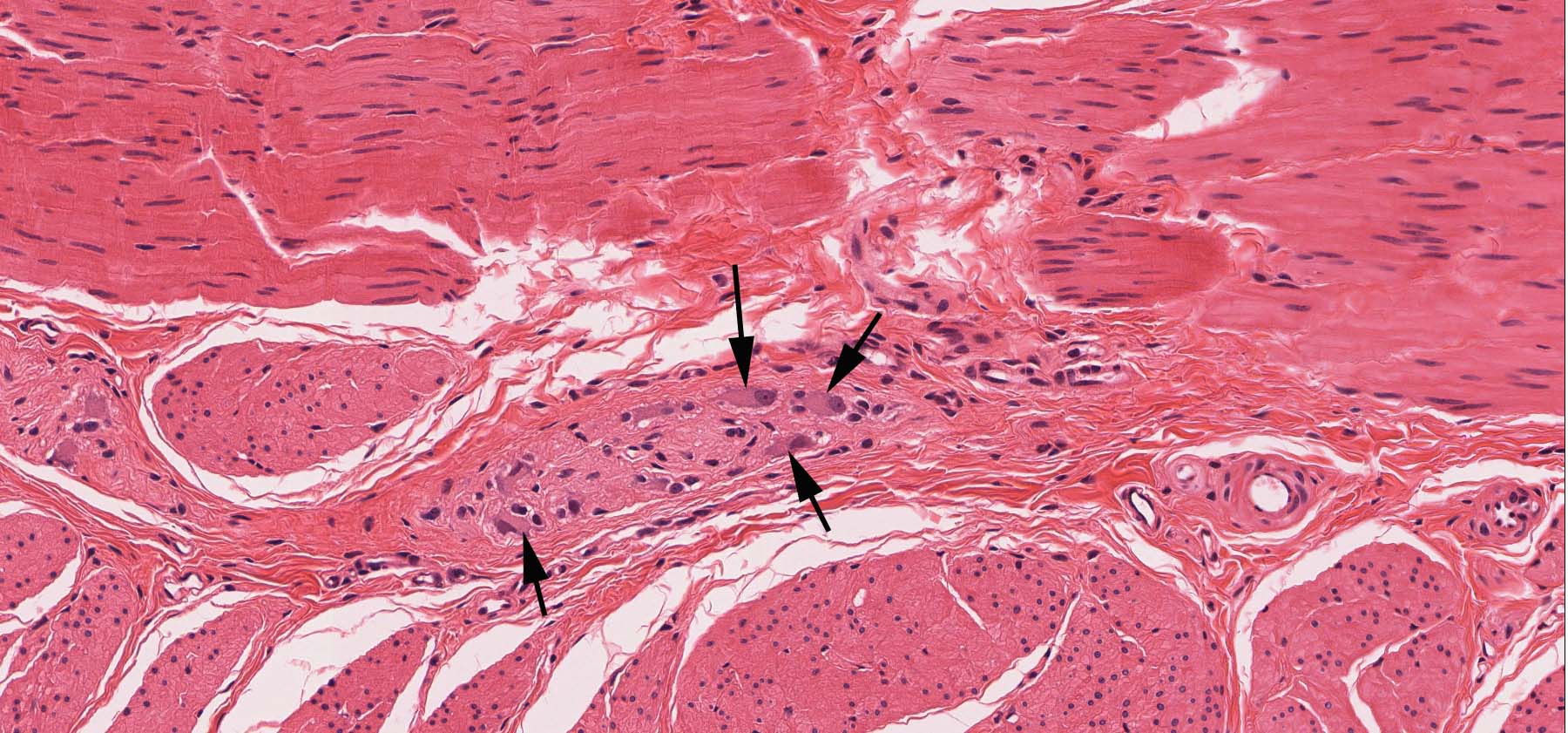
When the organs are stimulated by a prolonged stretch they cause the stretched muscle to relax. Conscious proprioception is transmitted in this pathway ie: Muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs which detect muscle length and contraction changes contributing to fine motor control and axial position.Ī reflex action mediated by the Golgi tendon organs that is called the inverse stretch reflex. Image 3: The dorsal column pathway is one of the neural pathways by which sensory information from the peripheral nerves is transmitted to the cerebral cortex. This causes a reflex inhibition of the muscle (see below).1.3C) and innervate premotor interneurons. Branches that enter the gray matter principally terminate in Rexed's laminae V–VII (Fig.Ib axons are fast conducting (72–120 m/s), bifurcate when entering the spinal cord, and send branches rostrally and caudally via the dorsal columns.Muscle contraction straightens the collagen fibers surrounding the GTO and compresses and depolarizes the sensory ending. Each GTO is innervated by a single myelinated Ib afferent.
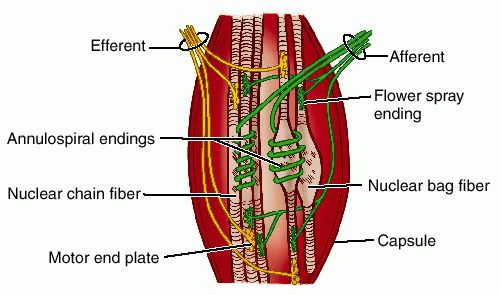
#Muscle spindle series
These receptors are located in series between the muscle fibers and the collagen strands that compose the tendon. GTOs are mechanoreceptors that provide output encoding the level of tensile load applied to the tendon.įor this reason, GTOs, particularly those in the lower-limb extensors, are critical for sensing the forces exerted to resist imposed loads or the force of gravity acting on the body and regulating extensor activity required for maintaining vertical support and postural stability. Accordingly, the tendon organ is considered to be a muscle tension receptor rather than a muscle stretch receptor. In contrast to muscle spindles, the Golgi tendon organ lies in series with skeletal muscle fibres and therefore discharges during passive stretching of the muscle as well as when the tendon is stretched by the contraction of the muscle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
